Radar and Radar-Warning Receivers
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the range,
angle, or velocity of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships,
spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain.
A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves
in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna
(often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a
receiver and processor to determine properties of the object(s).
Pulsed radio waves from the transmitter will reflect off the object
and are bounced back to the receiver.
By measuring the time delay between transmitted and received pulses, the
object's location and speed (relative to the transmitter) may be derived.
|
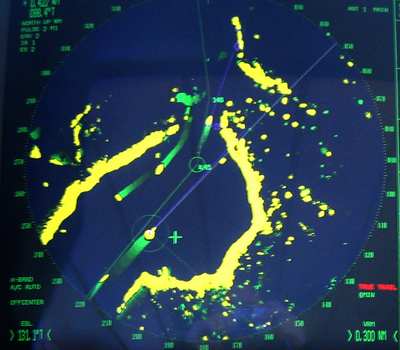 |
Marine radars on ships use microwaves in the X band (7-11 GHz) or S band (2-4 GHz).
They are used to detect other ships and land obstacles, to provide bearing and
distance for collision avoidance and navigation at sea.
Marine radars are electronic navigation instruments that use a rotating antenna
to sweep a narrow beam of pulsed microwaves around the water surface surrounding
the ship, detecting nearby objects by microwaves reflected from them.
This enables the radar receiver software to generate a picture of the ship's
surroundings on a display screen.
Radar is a vital navigation component for safety at sea and near the shore.
Navigators need to be able to maneuver their ships safely in the worst
of conditions and to be able to navigate "blind", when there is no visibility
at night or due to bad weather.
In addition to vessel-based marine radars, in ports or in harbours,
shore-based vessel traffic service radar systems are used by harbour masters
and the local coast guard to monitor and regulate ship movements in busy waters.
Nowadays, radars are rarely used alone in a marine setting. A modern trend is
the integration of radar with other navigation displays on a single screen,
as it becomes quite distracting to look at several different screens for
different kinds of information.
Therefore, displays can often overlay an electronic GPS navigation chart
of ship position, and a sonar or AIS display, on the radar display.
This provides a more complete and combined view of surroundings, in which
to maneuver the ship.
|
Radar-Warning Receivers
A Radar-Warning Receiver can detect the radio emissions of a radar systems.
Used offshore, their primary purpose is to issue a warning when a radar signal
is detected indicating a radar system on a nearby vessel.
Especially for small crews sailing offshore, a Radar-Warning Receiver may
contibute to marine safety by signaling the approach of a ship carring a radar system.
A Radar-Warning Receiver can be as simple as just detecting the presence of
transmitter energy in a specific radar band or more sophisticated if they are
additionally capable of classifying the source of the radar by the signal's
strength, phase and waveform type.
|
